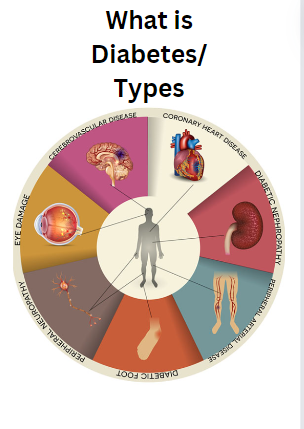
What is diabetes?
The questions people ask is; What is diabetes?. In a world where health is equated with wealth, understanding the most common health conditions is critical. One of the most common conditions in the world, diabetes affects millions of people. I will simplify the complexities surrounding diabetes by providing clear and concise information that will empower you to lead a healthier lifestyle.
What is diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes is a chronic illness characterized by high blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels. This essential material provides our bodies with their main source of energy. The hormone insulin, which comes from the pancreas and helps cells absorb and use sugar, keeps the delicate equilibrium in place. But in those who are struggling with diabetes, a disturbance in this balance takes shape.
The cause of the problem is a pancreas that is not producing enough insulin or is having trouble getting the body to use the insulin it does produce. As a result, too much sugar builds up in the blood, signaling the beginning of diabetes.
A sophisticated comprehension of the intricate relationship between insulin, blood sugar, and overall body function is necessary for managing this long-term illness. By removing the mystery surrounding diabetes, we open the door to well-informed strategies for controlling this medical condition and promoting a balanced, healthier lifestyle.
Types of Diabetes, there are three types of diabetes which are:
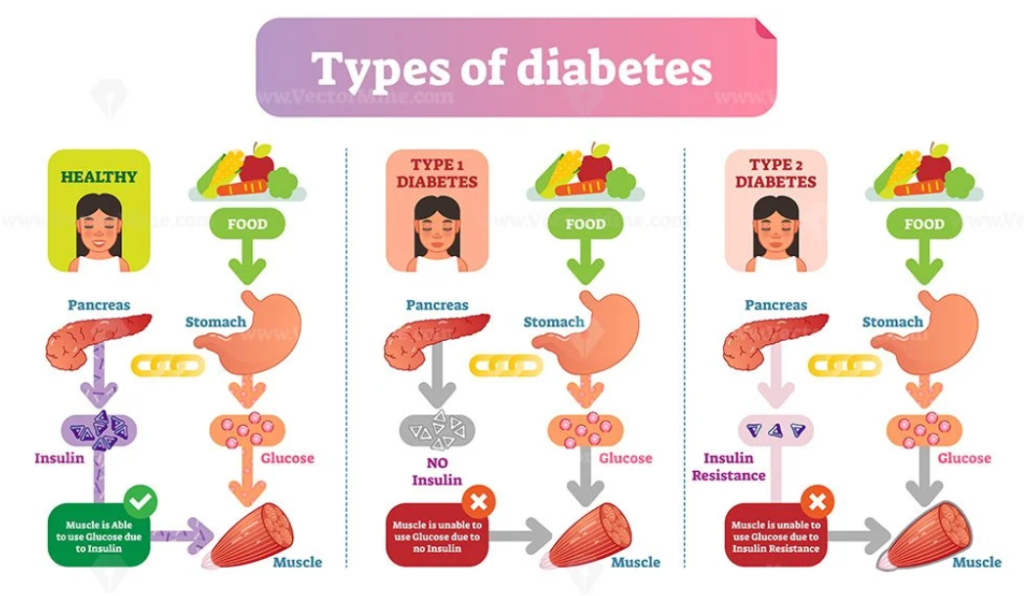
A. Diabetes Type 1:
Type 1 diabetes, which is usually detected in childhood or adolescence, is characterized by a distinct set of features. With this type of diabetes, the immune system launches an incorrect attack, mistakenly focusing on and destroying The cells found in the pancreas that produce insulin. The hormone insulin, which is essential for controlling blood sugar levels, is deficient as a result of this autoimmune reaction.
People who suffer from Type 1 diabetes are always in need of insulin injections to make up for the inadequate amount produced by their damaged pancreas. This external insulin administration becomes a lifesaver for preserving blood sugar levels at their ideal levels and the complex balance required for general health rather than just a treatment.
The complex dynamics of Type 1 diabetes require careful management and a sophisticated knowledge of the body’s insulin needs. Beyond the short-term health consequences, this illness frequently necessitates a special set of coping mechanisms and lifestyle modifications for both the afflicted individuals and their support systems. Through exploring the intricacies of Type 1 diabetes, we develop a more profound understanding of its obstacles, which in turn promotes compassion and knowledgeable assistance for individuals managing this specific aspect of the diabetes spectrum.
B. Diabetes Type 2:
Type 2 diabetes is a specific type of diabetes that primarily affects adults, though it is not limited to them. Insulin resistance, a condition that causes the body to less effectively use insulin, is the cause of Type 2 diabetes, as opposed to Type 1 diabetes, which is caused by the immune system attacking cells that produce insulin.
The body’s cells do not react to the hormone insulin, which is responsible for bringing glucose into cells for cellular energy production, as best they can in this metabolic complexity. This resistance starts a chain reaction that eventually raises blood sugar levels. Although genetic predispositions are a factor, lifestyle choices have a major impact on the onset and course of Type 2 diabetes.
A multitude of factors can influence the onset of Type 2 diabetes. of variables, the two most important ones being nutrition and exercise. Sedentary lifestyles and unhealthy food choices can both lead to the development of insulin resistance. On the other hand, leading a healthy, active lifestyle can be crucial to controlling or even preventing Type 2 diabetes.
Navigating Type 2 diabetes requires an understanding of the complex interactions between genetics, lifestyle choices, and metabolic complexities. Individuals and healthcare professionals can apply focused interventions that address both the condition’s underlying causes and immediate symptoms by acknowledging the complex nature of this illness.
C. Diabetes during pregnancy(also known as gestational diabetes):
Gestational diabetes, which only appears during pregnancy, adds a distinct facet to the range of diabetes and calls for a more thorough analysis of its consequences. This transient type of diabetes isn’t not only relevant to a mother’s health during pregnancy but also has implications for her health afterward.
Type 2 diabetes is more likely to develop later in life when gestational diabetes occurs. This condition’s temporal aspect—it manifests itself specifically during the gestational period—highlights the complex interplay between metabolic dynamics and reproductive health. Beyond its direct effects on the expectant mother, gestational diabetes is a sign of impending problems with her health after giving birth.
This pregnancy variation throws off the body’s normal balance of insulin utilization, which raises blood sugar levels. The consequences of gestational diabetes are not limited to the short term; the chance of developing Type 2 diabetes is a warning sign of the long-term effects of the condition. Both expecting mothers and healthcare professionals need to be aware of the subtleties of gestational diabetes. Proactively managing this condition can not only address immediate health issues, but also reduce the long-term risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. This all-encompassing method emphasizes how health problems are interconnected and stresses the importance of receiving holistic care both before and after pregnancy.
Identifying Diabetes Symptoms and Providing Efficient Care:
A thorough understanding of the common symptoms of diabetes is essential for both early detection and proactive management.
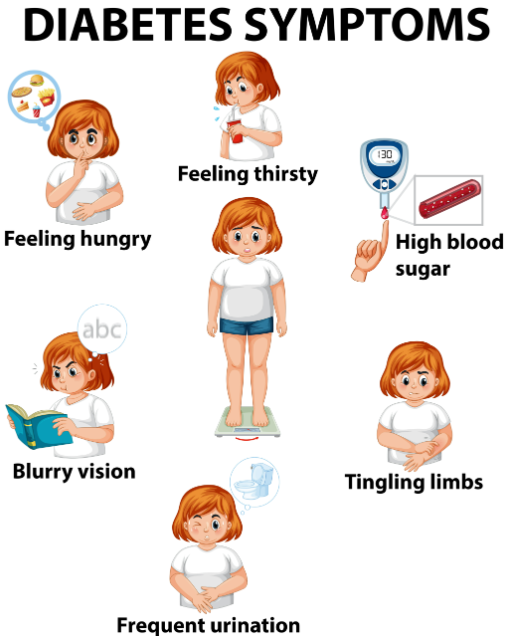
Typical signs include:
1. Often needing to urinate
2. Prolonged thirst 3. Inexplicable weight loss
4. Exhaustion
5. Haze
6. Slow-to-heal injuries
Why It’s Important to Understand Diabetes?
Understanding diabetes in depth is essential due to the possible consequences if untreated. Unmanageable Diabetes can cause serious side effects like:
1. Heart disease
2. Damage to the kidneys
3. Damage to the nerves
4. Eye issues and blindness
5. Conditions of the skin
6. Hearing loss
Useful Advice for Managing Diabetes:
1. A well-balanced diet that consists of whole grains, lean proteins, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
• Keep an eye on portion sizes to avoid overindulging.
• Limit your intake of processed and sugary foods.
2. Frequent Exercise:
- Perform physical activities such as swimming, cycling, or walking.
• Aim for 150 minutes or more per week of moderate-intense exercise.
• Before beginning a new exercise program, speak with a healthcare provider.
3. Medication and Insulin:
• Comply with your doctor’s instructions and take your prescribed medications as directed.
• Insulin may be required for some people, and precise administration is critical.
4. Consistent observation:
- Use a glucose monitor to check your blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
• Keep a journal so you can identify trends and make necessary changes to your management strategy.
5. Handling Stress:
• Use stress-relieving methods like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing.
• Acknowledge that stress can affect blood sugar levels and stress the value of developing healthy coping strategies.
In summary
Gaining knowledge about diabetes can be a life-changing experience that empowers people to take charge of their health and make well-informed lifestyle choices. By adhering to a balanced diet, regularly exercising, and practicing effective stress management, people with diabetes can not only live fulfilling lives but also greatly reduce their chance of complications.
It’s important to understand that even a little knowledge can have a big impact. in encouraging a happier and healthier lifestyle. Making the decision to be conscious and proactive turns into a beacon that points people in the direction of a vibrant, well-being-marked path. When it comes to diabetes, information really is a powerful ally that can help you achieve a future full of happiness and health.