When trying to lead a healthy lifestyle of prebiotic foods list, the terms “probiotics” and “prebiotics” are frequently encountered. Prebiotics are essential for feeding the good bacteria that probiotics are known to contain and which promote gut health. To assist you in achieving a healthy and balanced gut microbiome, we will explore the world of prebiotics in this comprehensive guide and provide you with a long list of prebiotic foods.
Recognizing Prebiotics
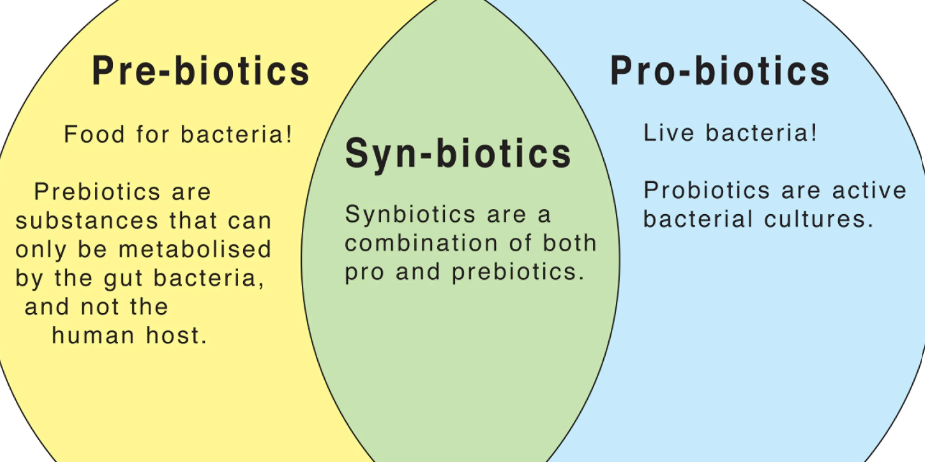
Prebiotics: What Are They?
Let’s first review what prebiotics are before moving on to the list of foods that contain them. Prebiotics are indigestible fibers that provide nourishment to the probiotics, or good bacteria, that live in our digestive systems. By encouraging the growth and activity of these beneficial bacteria, these substances support the development of a healthy gut flora.
The Value of a Balanced Gut Microbiota
General health depends on a gut microbiome that is in balance. In addition to helping with digestion, it is essential for immune system performance, nutrient absorption, and even mental health. Prebiotics play a major role in preserving this delicate equilibrium.
“10 Incredible Benefits of Prebiotic Foods”
Prebiotic foods have become unsung heroes in the field of nutrition and wellness, offering a host of advantages to health that go beyond the digestive tract. Let’s explore the amazing realm of prebiotic foods and discover ten noteworthy advantages that make them necessary for a robust and healthy body.
1. Enhanced Digestive Wellbeing
The primary advantage of prebiotics is their capacity to promote intestinal well-being. Prebiotics support the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria by acting as a selective fuel for them. Consequently, this improves digestive health overall, facilitates the absorption of nutrients, and lessens common digestive problems like constipation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
2. A Wide Range of Microbial Ecology
Prebiotics encourage the growth of different strains of beneficial bacteria, which adds to the diversity of the gut microbiome. Improved nutrient metabolism, overall gut balance, and resistance to infections are all linked to a diverse microbial ecosystem.
3. Strengthening of the Immune System
Prebiotics also have an impact on the immune system, where they are essential for regulating immune responses. Prebiotics help maintain a healthy immune system by promoting the synthesis of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) during fermentation, which lowers the risk of infection and increases immune resilience in general.
4. Weight Management
Prebiotic foods are a great source of support for people who are dieting. These foods have been connected to improvements in the hormones in the gut that control hunger, fullness, and energy equilibrium. Prebiotics may help with weight loss and maintaining a healthy body weight.
5. Mental Health and Mood
The relationship between gut health and mental well-being has been revealed by recent research. Prebiotics, by influencing the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, contribute to mood regulation. Consuming a diet high in prebiotic foods may have a positive effect on mental health, possibly reducing symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression.
6. Enhanced Absorption of Nutrients
Prebiotics improve the body’s ability to absorb vital nutrients, which benefits general health. Prebiotics produce organic acids through fermentation, which improves the solubility of minerals like magnesium and calcium. Better absorption and utilization of these essential nutrients are made possible by their increased solubility.
7. Sufficient Levels of Blood Sugar
There has been evidence linking specific prebiotic fibers, like inulin, to increased insulin sensitivity. Prebiotic foods can help control blood sugar levels, which is why they are advantageous for people trying to manage or avoid diseases like diabetes.
8. Decreased Inflammation
Many chronic diseases share a common factor: chronic inflammation. Prebiotics help control inflammation by encouraging the development of good bacteria and the synthesis of SCFAs, which are anti-inflammatory fatty acids. Conditions linked to chronic inflammation can be prevented and managed with the aid of this anti-inflammatory effect.
9. Heart Health Assistance
Prebiotics have the potential to improve cardiovascular health by having a beneficial effect on blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Prebiotics ferment to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have been associated with improvements in cardiovascular markers and may lower the risk of heart disease.
10. Better Skin Health
Prebiotic benefits also include the intriguing gut-skin connection. Prebiotics can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which can lead to better skin. Prebiotics may aid in the management of skin conditions and the promotion of a clear complexion by lowering inflammation and enhancing nutrient absorption.
prebiotic foods list are as follow:

Let’s now examine a wide variety of prebiotic-rich foods that you can simply include in your regular diet.
A. High in Fiber Vegetables
Artichokes: A rich source of the powerful prebiotic fiber inulin.
B. Leeks: Packed with resistant starch and inulin.
Garlic: Has fructooligosaccharides (FOS) and inulin.
C. Fruits
A good source of resistant starch is found in bananas.
Berries: Rich in fiber, which supports digestive health.
Kiwi: Packed with prebiotic enzymes and fibre.
D. Complete Grains
Oats: A fantastic source of the prebiotic fiber known as beta-glucans.
Barley: High in arabinoxylan and beta-glucans.
Quinoa: Provides a prebiotic effect due to its insoluble fiber content.
E. Legumes
Lentils: Rich in fiber and resistant starch.
High in soluble fiber, chickpeas promote gut health.
Black beans: Contains oligosaccharides and resistant starch.
F. Seeds and Nuts
Almonds: Offer prebiotic potential and fiber.
Rich in soluble fiber, flaxseeds nourish gut flora.
Chia seeds: Insoluble and soluble fiber are present.
G. Tubers
One source of resistant starch is sweet potatoes.
Jicama: Packed with prebiotic fiber, inulin is present.
Artichokes from Jerusalem: Rich in inulin.
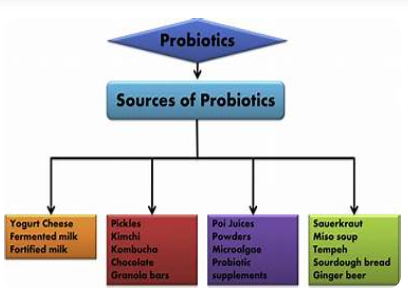
H. Milk
Yogurt: In addition to providing probiotics, yogurt also has prebiotic ingredients.
Kefir: A dairy product that ferments and contains probiotics.
Adding Prebiotic Foods to Your Diet: A Gradual Overview
Consuming more foods high in prebiotics should be done gradually. Even though there are many health benefits associated with these foods, abrupt changes in the amount of dietary fiber consumed may cause discomfort like gas or bloating. Gradually increase the quantity of prebiotic foods over time, starting with small amounts. By taking this approach, you can minimize any potential digestive issues and help your digestive system adjust to the new dietary fiber.
Various Diet
To fully benefit from prebiotics, it is imperative to maintain a varied diet. Various prebiotic foods support different types of good bacteria in the gut. Try to arrange your plate in a vibrant and diverse way by including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and tubers. You can be sure you’re giving your gut’s varied microbial population a wide spectrum of nutrients by experimenting with different prebiotic sources.
Cooking Methods
Foods high in prebiotics may lose some of their prebiotic content during cooking. Certain prebiotics may be more sensitive to heat than others. When adding prebiotic foods to your diet, take into account the following cooking techniques:
Unprocessed Ingestion
Eating raw prebiotic foods can be a great way to maintain their natural prebiotic content. There are foods that are best enjoyed raw, such as fruits, vegetables, and some nuts and seeds. But remember that not everyone should consume raw food, particularly if they have digestive sensitivities.
Gentle Steaming
Vegetables high in probiotics can retain their nutritional value by steaming them gently. Broccoli, asparagus, and green beans are among the vegetables that can be softened without losing their prebiotic fibers by gently steaming them. Steer clear of overcooking as this could degrade some of the prebiotic compounds.
Cooking
Prebiotic vegetables can be made more palatable and flavorful by sautéing them in a small amount of healthy oil. Utilize oils with added health benefits, such as coconut or olive oils. To preserve the prebiotic content, cook for a brief period of time.
The process of fermentation
Although fermentation is primarily used as a preservation technique, it can also increase a food’s prebiotic content. Pickles, kimchi, and other fermented foods can be beneficial supplements to your diet since they contain probiotics and prebiotics.
Cooking and Snacking
You can add some prebiotic-rich foods, like sweet potatoes or oats, to baked or roasted foods. These cooking techniques preserve the prebiotic qualities of the food while giving it a new dimension in terms of flavor and texture.

Conclusion
Including foods high in prebiotics in your diet is a tasty and practical approach to maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Through comprehension of the advantages and investigation of the varied list of prebiotic foods furnished, you can initiate a voyage towards enhanced immunity, better digestion, and general wellness. Savor the journey of tasting new flavors and feeding your body to become a healthier, happier version of yourself from the inside out.





